When you use to automatically calculate a dimension size the dimensions that you do explicitly specify must divide evenly into the number of elements in the input matrix numel a.
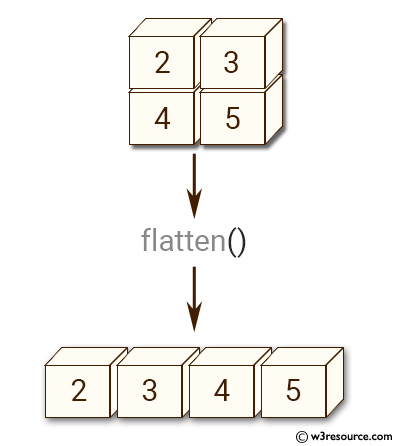
How to flatten a matrix in matlab.
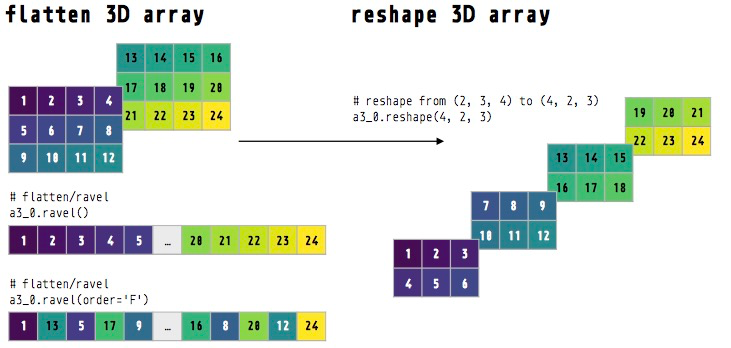
For example reshape a 3 2 1 1 produces a 3 by 2 matrix.
A matrix is a two dimensional array of numbers.
R reshape m 1.
Unlike some languages matlab does not have any concept of 1d arrays.
Beyond the second dimension the output b does not reflect trailing dimensions with a size of 1.
Similar questions and discussions.
Create a matrix a and sort each column of a in ascending order.
R will convert m into a single row.
For example let us create a 4 by 5 matrix a.
For example reshape a 3 2 1 1 produces a 3 by 2 matrix.
Beyond the second dimension the output b does not reflect trailing dimensions with a size of 1.
Can you help by adding an answer.
For example if the input to the layer is an h by w by c by n by s array sequences of images then the flattened output is an h w c by n by s array.
When you use to automatically calculate a dimension size the dimensions that you do explicitly specify must divide evenly into the number of elements in the input matrix numel a.
M matlab matrix.
A flatten layer collapses the spatial dimensions of the input into the channel dimension.
When you use to automatically calculate a dimension size the dimensions that you do explicitly specify must divide evenly into the number of elements in the input matrix numel a.
For example reshape a 3 2 1 1 produces a 3 by 2 matrix.
All arrays have atleast 2 explicit dimensions and infinite implicit trailing singleton dimensions.
In matlab you create a matrix by entering elements in each row as comma or space delimited numbers and using semicolons to mark the end of each row.
Sorting the data in an array is also a valuable tool and matlab offers a number of approaches.
How to flatten a matrix in row major order.
For example the sort function sorts the elements of each row or column of a matrix separately in ascending or descending order.